Trust Management between Systems
Digitalization is leading us towards a future where people, systems and things are not only interacting with each other, but might start forming societies on their own.
In these dynamic systems enhanced by artificial intelligence, trust management on the level of human-to-machine as well as machine-to-machine interaction becomes an essential ingredient to supervise safe and secure progress of our digitalized future.
Main goal: Building Trust in Smart Dynamic Ecosystems
Challenges of Trust Management Smart Dynamic Ecosystems
- Situational Scope of Trust: high dependence of trust building on the context of trustor
- Subjectivity of Trust: influence by the factors inherent to the trustor (e.g. in taking risks)
- Default Trust Score of New Agents: on which trust score shall a new agent start
- Trust Erosion: trust score is subject to decay in case of no or too few interactions
- Detection of Hidden Malicious Intentions: hard to detect, likely to make mistakes in detection
- Safety Assurance in Face of Untrusted Agents: an ingredient of immune-response capability



The research focuses on different areas:
-
System-to-System Trust (update scenario): A vehicle is downloading a black-box update at runtime. May I trust that update and give it access to my critical driving functions?
-
System-to-System Trust (collision avoidance scenario): Two vehicles approaching each other. May I trust the other vehicle that it does not intend to cause a crash?
- Trust-Based Adaptive Safety: How shall I adapt my safety mechanisms to the level of trust? What if I misdudge trust (false postivies/negatives)?
- Trust Management and Governance: What mechanisms (e.g., incentives, evidence collection, reparation) shall be in place to protect and govern trust values?
Behaviour-predictive Trust in Autonomous Drone Swarms
A model to predict the level of trust between drones in drone swarms. We proposed a trust-assurance method for autonomous drones utilizing runtime compliance checking via a Digital Twin (DT). The DT incorporates drone-specific metrics from AirSim simulations, including sensors' health and network centrality for real-time behavior analysis. Drones collaborate in swarms, sharing predictive and actual behaviors for trust assessment. The model uses Random Forest (RF), Support Vector Regression (SVR), and Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to estimate swarm coordination rates as trust indicators, with each iteration classifying drones as Trusted or Malicious. The model was tested in an autonomous drone delivery system against various trust-related attacks, demonstrating SVR’s effectiveness in estimating coordination rates and RF and SVM's role in trust classification.

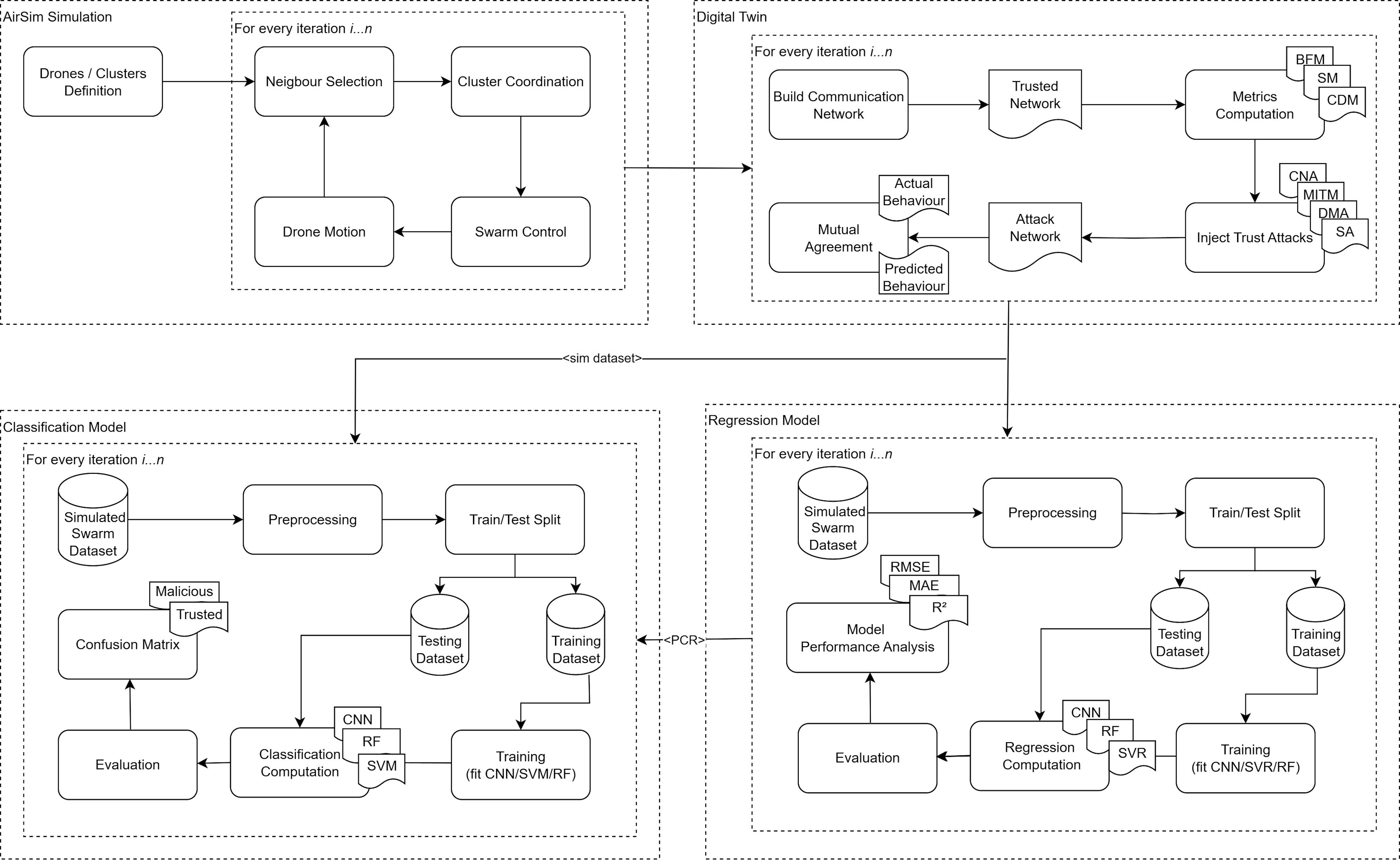
IQBAL, Danish; Hind BANGUI and Bruno ROSSI. Trial by Twin: Behavior-Predictive Trust in Autonomous Drone Swarms. In Springer. The 31st International Conference on Cooperative Information Systems (CoopIS). 2025.
Trust Governance Mechanisms
Smart dynamic ecosystems that integrate digital agents, physical infrastructure, and human-technology interactions need to foster partnerships among their members to collaboratively tackle complex tasks. This requires the establishment of trust and effective governance mechanisms at the ecosystem level, which are essential for ensuring proper functioning, safety, and compliance with established rules. However, there is currently limited understanding of what trust-supporting governance mechanisms might look like. We aim to explore this promising area of research by compiling a taxonomy of governance mechanisms designed to facilitate trust management in smart dynamic ecosystems. The aim is to develop a comprehensive governance model to help with the complex and dynamic nature of these ecosystems.
- Trust score calculation, propagation, update
- Incentives, i.e., rewards and punishment mechanisms
- Reparation and redemption mechanisms
- Evidence collection
- Pre-incident to predict somebody is attempting misbehaviour
- Post-incident to either identify the source of misbehaviour, or to understand whether a corrective action needs to be taken
KUŠNIRÁKOVÁ, Daša and Barbora BÜHNOVÁ. Taxonomy of Governance Mechanisms for Trust Management in Smart Dynamic Ecosystems. Online. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering. Setubal, Portugal: Scitepress, 2024, p. 700-710. ISBN 978-989-758-696-5.

The context of a Trust Management governance model







