Semantic BMS Framework
Overview
Facility benchmarking and evaluation of facility performance are crucial tasks in reaching efficient, economical, and sustainable facility operation. Modern, smart buildings automate operation of installed technologies (e.g. Heating, ventilation, air conditioning -- HVAC) and provide remote monitoring and control of them. Smart building are typical applications of cyber-physical systems, in this case represented by building automation systems (BAS) and Building Management Systems (BMS). The systems contain vast numbers of various sensors that can be utilized in performance assessment. However, they lack convenient tools for data inspection, which limits their use in building performance and efficiency analysis and benchmarking especially on large sites.
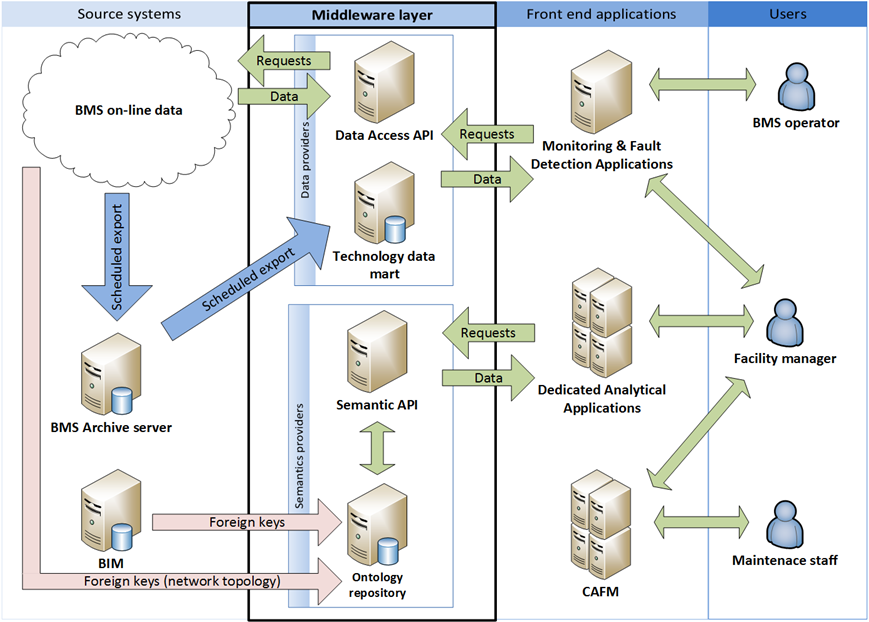
The SBMS framework is a middleware layer designed to enrich BAS data with additional semantic information. As a model, adaptation of Semantic Sensor Network (SSN) ontology for the field of building operation analysis is used. The framework provides convenient ways for querying the model and allows facility managers to conveniently use BAS data for benchmarking and decision support.
Methods and principles
- Service oriented architecture
- RESTful API
- JSON serialization
- RDF and SPARQL
- Ontologies via Ontology Web Language
Key development considerations and principles
- Modular architecture
- Data security
- Open Source components
- Automation protocol independency
Use case
The project of the Building Management System (BMS) that spreads over the whole Masaryk University (MU) and its facilities started together with the construction of the first part of the University Campus in Brno-Bohunice (UCB) that was completed in 2007. Since then, all the newly built facilities at the UCB have been connected to the BMS of MU. Additionally, other buildings spread through the city of Brno were connected to the system at the occasions of replacing an obsolete building equipment with new units. Other projects under construction are planned to be connected to the BMS of MU in the next few years. The core of the system is formed by devices and application servers that communicate over the BACnet protocol, which is briefly introduced later in this chapter. BMS of MU today contains over 1500 BACnet-enabled devices from more than 20 industry-leading vendors.

Selected publications
KUČERA, Adam a Tomáš PITNER. Intelligent Facility Management for Sustainability and Risk Management. In Hřebíček, J.; Schimak, G.; Kubásek, M.; Rizzoli, A.E.. Environmental Software Systems. Fostering Information Sharing. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer, 2013. pp. 608-617, 10 p. ISBN 978-3-642-41150-2. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-41151-9_57.
KUČERA, Adam; PITNER, Tomáš. Semantic BMS: Ontology for Analysis of Building Automation Systems Data. In: DOCEIS 2016: Technological Innovation for Cyber-Physical Systems. 2016, vol.470/2016. IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology. pp. 46-53, 8 p., ISBN 978-3-319-31164-7. ISSN 1868-4238.



